近日,由我校特聘院士姚建铨、光电工程学院梁兰菊教授共同指导的博士杨茂生在太赫兹生物传感器方面的研究工作取得新进展,相关成果发表在国际期刊《Optics EXPRESS》上。梁兰菊教授、张璋博士为文章的共同通讯作者,联合培养博士杨茂生为第一作者。
团队提出了一种基于电磁诱导透明的超构材料太赫兹生物传感器,并应用在检测不同浓度的非癌细胞浓度等方面。该结构同时存在强辐射损耗的偶极子(明模)共振与非辐射损耗的四偶极子(暗模)的共振模式。基于谐振子耦合模型理论得到了不同浓度的肺癌细胞以及不同折射率的介质层对结构共振特性的影响。实验结果表明,设计的超构材料生物传感器能够非常灵敏的检测癌细胞浓度,研究结论可为开发新型的快速、无标记及高灵敏的超构材料生物传感器提供参考。
上述研究成果得到了国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFA0700202, 2017YFB1401203)、国家自然科学基金(61701434, 61735010)、山东省自然科学基金(ZR2017MF005,ZR2018LF001 )、枣庄市自主创新及成果转化项目基金(2016GH19, 2016GH31)、山东省高等学校科技计划项目基金(J17KA087)等项目的资助。
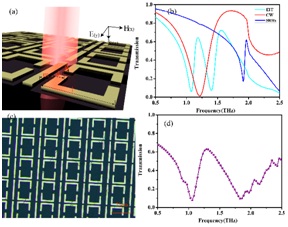
Fig. 1. The schematic illustration and performance of biosensor based on the EIT-like MMs. (a) The periodic structure and diagram of the EIT-like MMs. The geometrical parameters are g=13.5 µm, d=3.5 µm, m=15 µm, l= 75 µm, respectively (b) Simulated transmission spectra of the EIT-like MMs, CW and the SRRs (c) The micrograph of the fabricated EIT-like MMs with A549. (d) Experimentally measured transmission spectra of the EIT-like MMs.
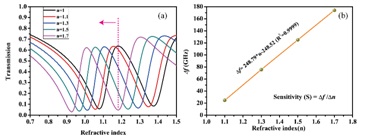
Fig. 3. (a) The effect of transmission on refractive index of the analyte with the thickness of 11 µm. (b) The frequency shift with the refractive index of analyte extracted from (a).
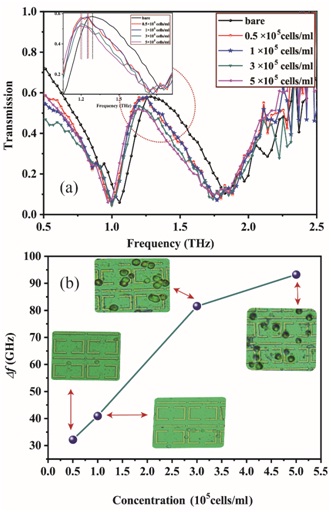
Fig. 4. (a) The effect of transmission on cell concentration ranging from 0.5×105 to 5×105 cells/ml. (b) The frequency shift with cell concentration ranging from 0.5×105 to 5×105 cells/ml.
文章链接网址:
https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/abstract.cfm?uri=oe-27-14-19520&origin=search